Input Data : Transactional Data(거래가 이루어진 데이터)
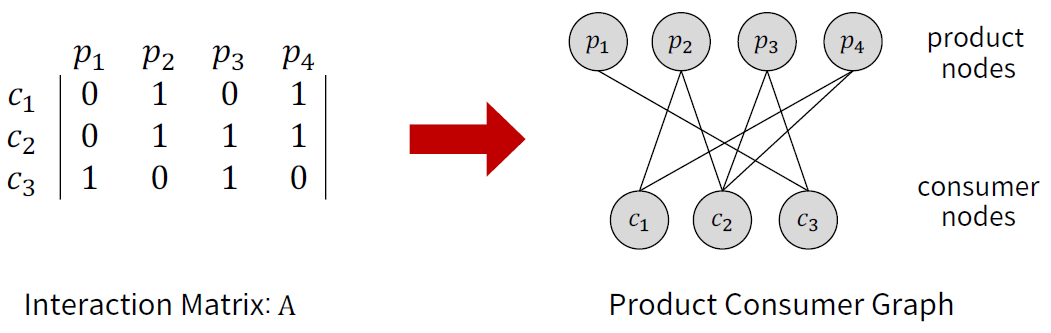
-> Consumer와 product 사이의 관계를 Matrix&Graph로 표현
6 Types of CF(Collaborative Filltering) for e-Commerce Recommendation
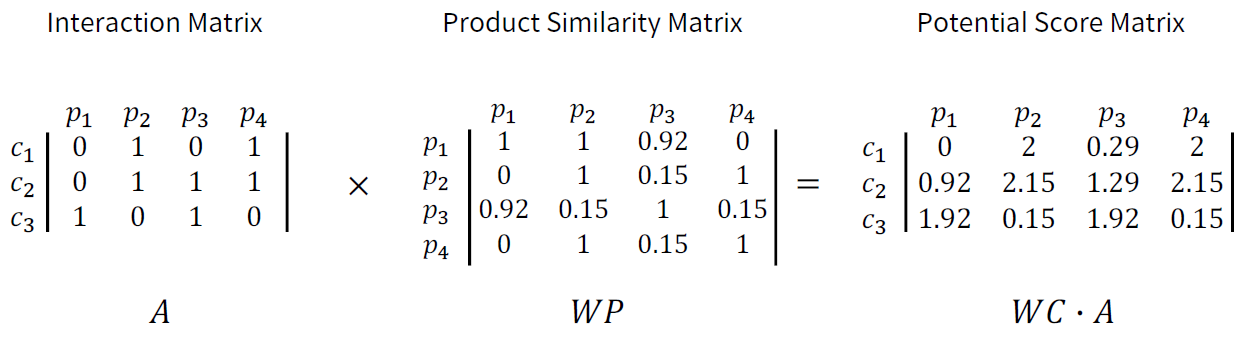
1. User-based
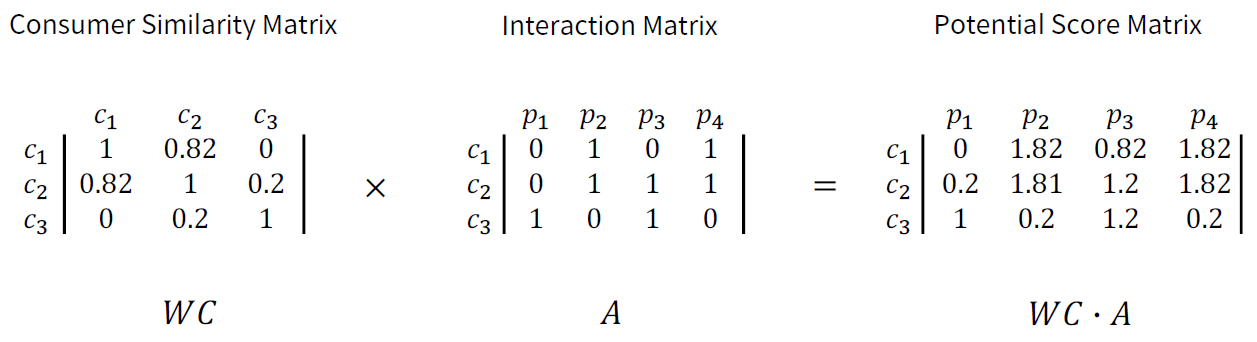
2. Item-based
Sparsity 문제를 해결하고자 하는 방식들
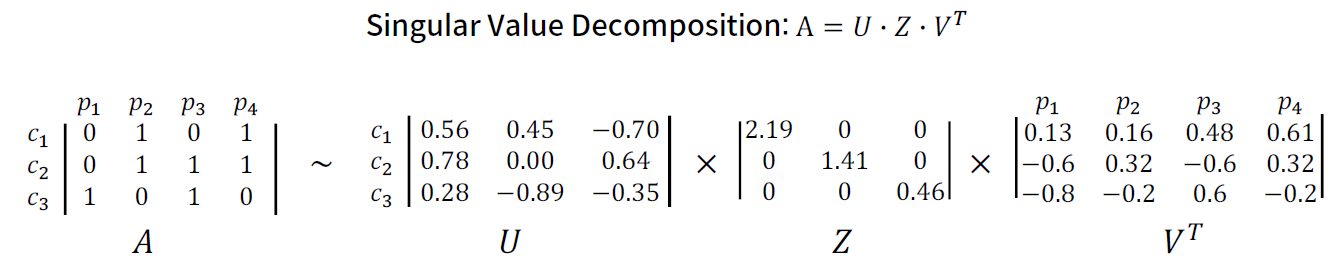
3. Dimensionality Reduction

4. Generative Model(확률적 접근 방법)
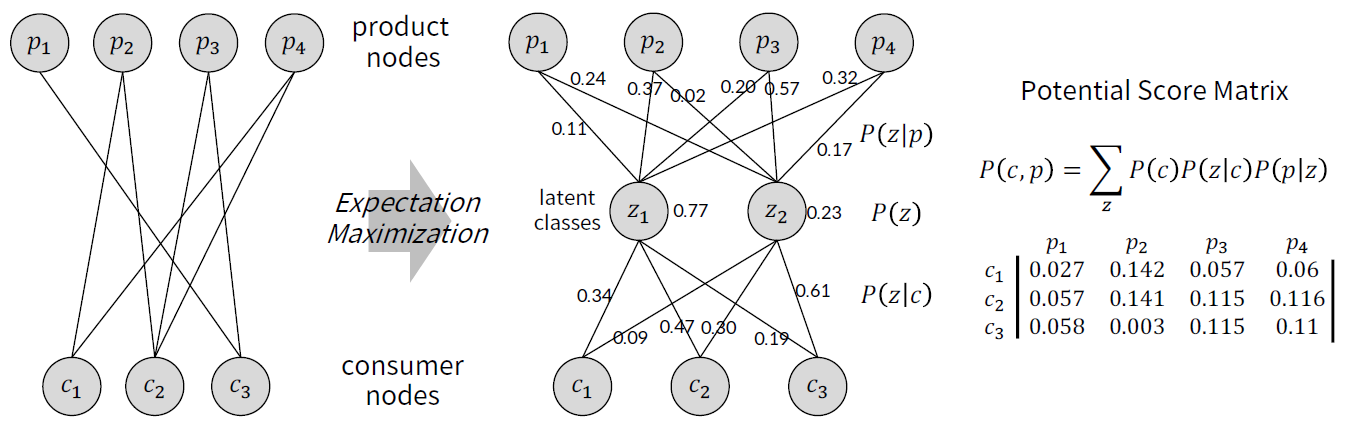
5,6. Graph-based Recommendation(그래프 특성을 활용한 접근 방법)
Concept : 그래프에서의 연결 정보들을 탐색하면 잠재된 연결성을 찾을 수 있다.
[연결정보를 다루는 방식]
5. Spreading Activation
6. Link Analysis (PageRank(google), HITS)
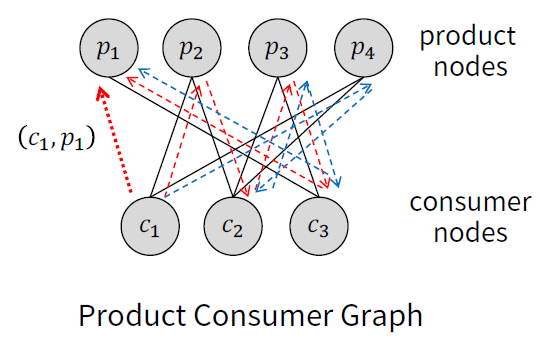
-> Link 정보를 반복적으로 따라가면 결국 수렴하는 값을 찾을 수 있다.
5. Spreading Activation : Hopfield Algorithm
: 추천 대상을 기점으로 시작하여 활성 상태를 전파해 나가고, 수렴하면 중지
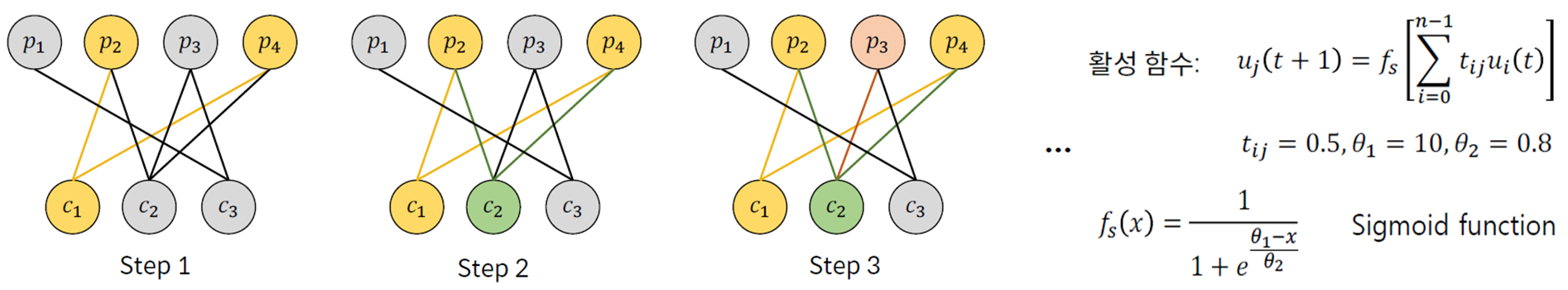
6. Link Analysis
: PageRank, HITS 등 웹페이지 랭킹 알고리즘을 추천에 적용
* HITS : 두가지 유형의 스코어를 반복적으로 계산하여 웹페이지 스코어링
[두가지 속성]
- Authoritative pages : 좋은 정보를 담고 있는 페이지
- Hub pages : authoritative에 대한 많은 링크를 담고 있는 페이지

= hub score의 합
= authority의 합
- 임의 값에서 시작하여 여러번 반복 계산하며 a,h는 일반적으로 수렴한다.
[Product와 consumer 그래프에 맞도록 변형, 개인화]


CR(0) : user의 활성 상태로 계속해서 바뀌는 Matrix
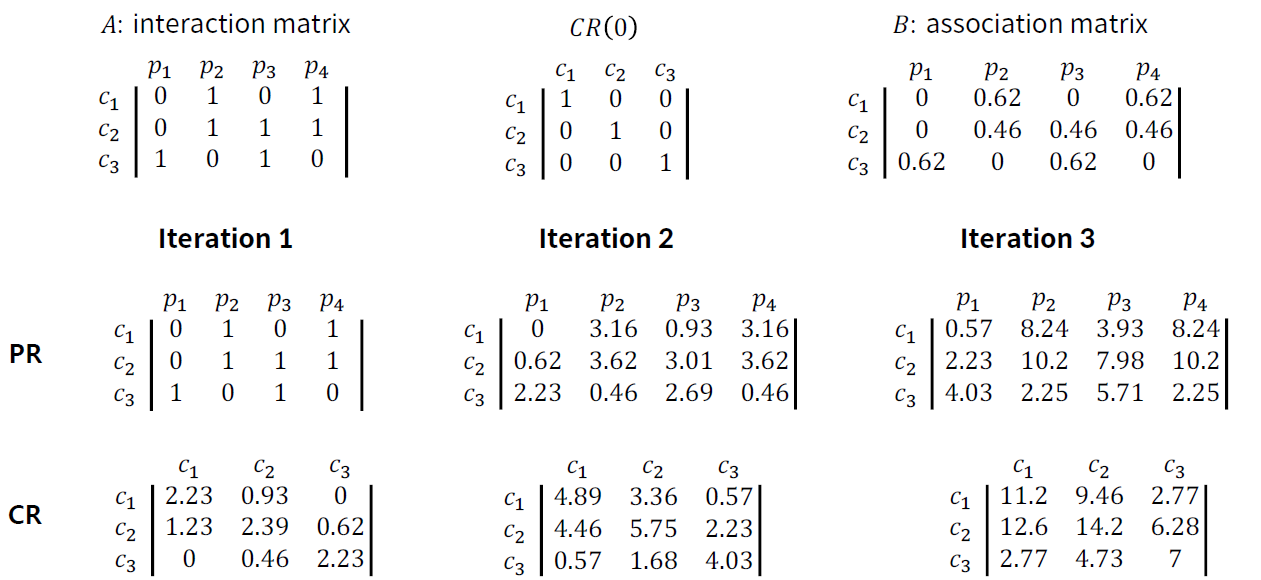
Random Walks with Restart for Personalized Recommendation
Random Walks for Recommendation
: 그래프 추천의 간단한 버전으로 개인화가 아닌 글로벌한 방법
- 시작 노드(consumer)에서 여러 노드로 일정한 확률로 이동한다고 했을 때, 각 노드(product)에 도달할 확률을 이용하여 추천
- 웹에서는 웹페이지간 전이만 존재하지만, 추천에서는 consumer와 product라는 두 가지 다른 유형의 노드에서의 전이로 변환된다.
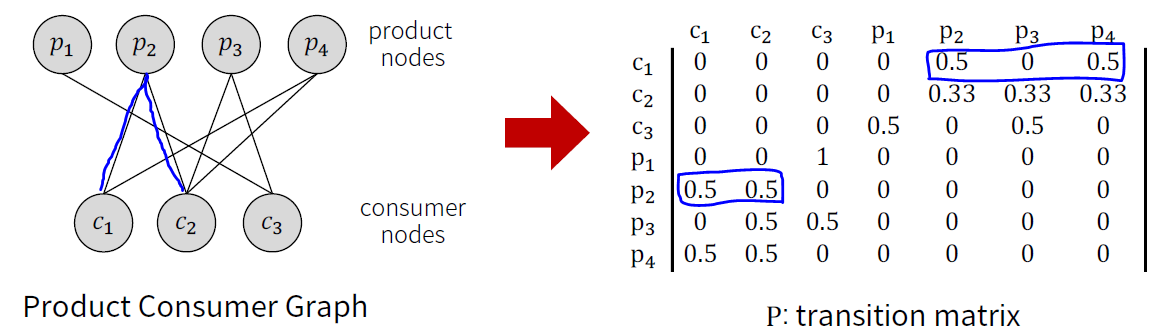
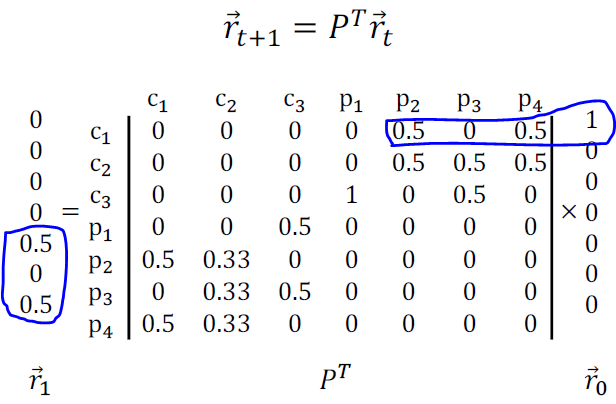
Random Walks
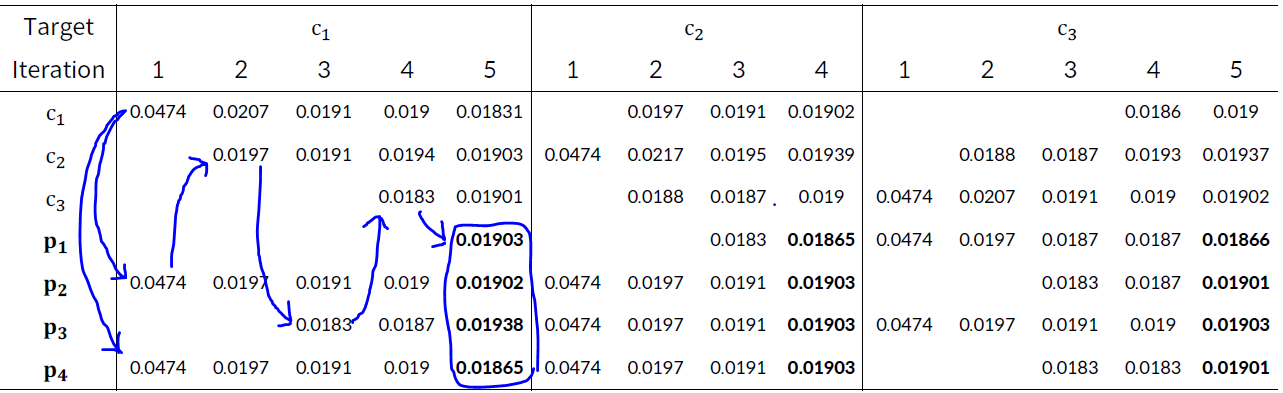
: r을 각 노드에 도달할 확률을 가진 벡터라고 하면 전이를 통해 지속적으로 변화하며 최종적으로는 수렴하게 된다.
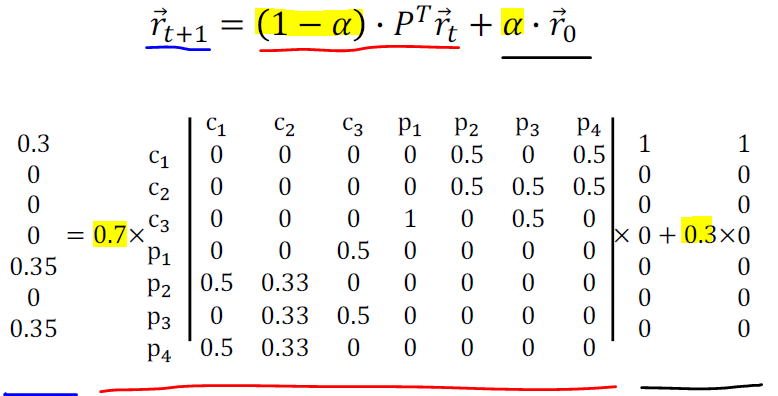
Random Walks with Restart
: 초기 시작점에서 시작할 확률을 추가로 고려하여 개인화 특성을 강화
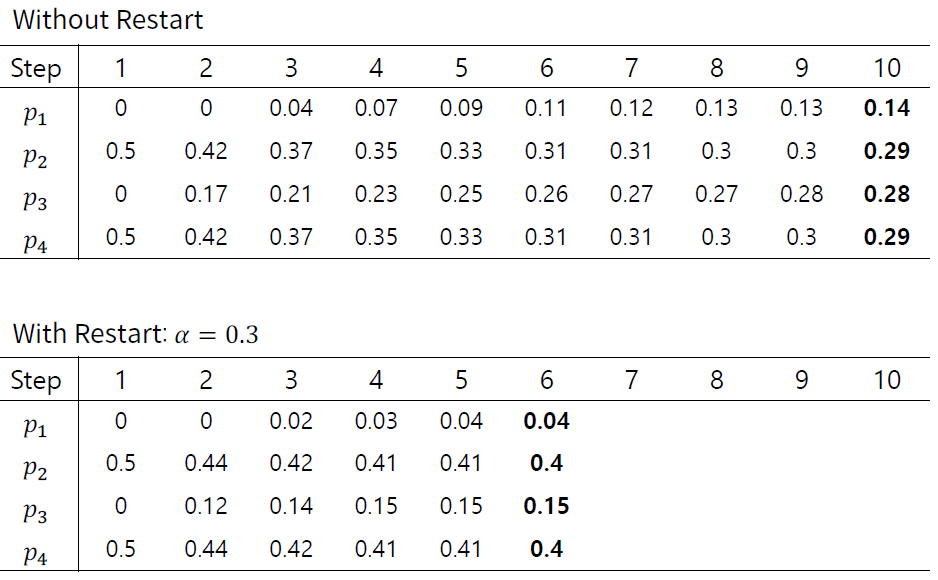
실습
- 커머스 데이터를 활용한 Random Walk Simulation
- Random Walk를 그대로 진행하면 속도가 느리기 때문에, Top N개의 node만 유지
- Event log로부터 Transition Matrix 생성
- 7 hop random walks
(User->Item->User->Item->User->Item->User->Item)
Random Walk with Restart on sample data
import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(precision=4, linewidth=120)
# page 36 싱습 데이터
matrix = np.array([
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0.5, 0, 0.5],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1/3, 1/3, 1/3],
[0, 0, 0, 0.5, 0, 0.5, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0.5, 0.5, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0.5, 0.5, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0.5, 0.5, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
])
r0 = np.array([1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
r = r0
a = 0.3
# 반복문을 늘려가면서 수렴하는 경우를 찾기
for i in range(0, 30):
# restart 하는 경우
if i % 2 == 1:
r = (1-a)*np.matmul(matrix.T, r) + a * r0
else:
r = np.matmul(matrix.T, r)
if i % 2 == 0:
print(f'{i:2d} {r}')
Random Walk on Commerce Data
- Create Transition Matrix Tables
%%sql
-- user의 score값을 transaction matrix로 활용
drop table if exists cmc_user_product_prob;
create table cmc_user_product_prob as
with events as (
select
user_no,
item_no,
case
when event_name = 'purchase_success' then 4
when event_name = 'add_to_cart' then 3
when event_name = 'like_item' then 2
else 1
end event_weight,
pow(0.9, (date_part('day', to_timestamp('2021-07-25', 'YYYY-MM-DD') - event_timestamp) * 24 + date_part('hour', to_timestamp('2021-07-25', 'YYYY-MM-DD') - event_timestamp))/12) time_weight
from cmc_event
where event_timestamp between '2021-07-18' and '2021-07-25' )
-- transaction probability 계산
select user_no, item_no,
w / (sum(w) over (partition by user_no)) prob, -- user에서 item으로 갈 때의 확률
w / (sum(w) over (partition by item_no)) r_prob -- item에서 user로 갈 때의 확률
from (
select user_no, item_no, sum(event_weight * time_weight) w
from events
group by user_no, item_no ) t;
-- index값 만들기
--user에서 item으로
create index idx_cmc_user_product_prob_1 on cmc_user_product_prob (user_no, item_no, prob);
--item에서 user로
create index idx_cmc_user_product_prob_2 on cmc_user_product_prob (item_no, user_no, prob);
- Set Test User
user_no = '++MXKfwkOw4VFn9HkVCRrw=='
# TOP N개만 활용(다 활용하면 너무 느려짐)
max_cand_size = 1000
- Random Walk Simulation
a = 0.5
for step in range(1, 20):
query = f'''drop table if exists cmc_rwr_step{step}'''
executeQuery(query)
# r0에 대해서 (초기화 단계) user에서 item으로 transaction
if step == 1:
query = f'''
create table cmc_rwr_step{step} as
select item_no, prob
from cmc_user_product_prob
where user_no = '{user_no}'
order by prob desc
limit {max_cand_size}
'''
# item에서 user로 transaction
elif step % 2 == 0:
query = f'''
create table cmc_rwr_step{step} as
select user_no, sum(a.r_prob*b.prob) prob
from cmc_user_product_prob a join cmc_rwr_step{step-1} b on b.item_no = a.item_no
group by user_no
order by prob desc
limit {max_cand_size}
'''
# restart해서 user에서 item으로 transaction하는 과정
else:
query = f'''
create table cmc_rwr_step{step} as
select item_no, sum(prob) prob
from (
select item_no, sum(a.prob*b.prob)*{1-a} prob
from cmc_user_product_prob a join cmc_rwr_step{step-1} b on b.user_no = a.user_no
group by item_no
union all
select item_no, prob*{a}
from cmc_user_product_prob
where user_no = '{user_no}' ) t
group by item_no
order by prob desc
limit {max_cand_size}
'''
executeQuery(query)
# 각 단계마다 결과 확인 초기화 단계와 restart 단계에서만 transaction data가 만들어지므로 그 부분에서만 display
if step % 2 == 1:
query = f'''
select a.prob, b.*
from cmc_rwr_step{step} a join cmc_product b on a.item_no = b.item_no
order by a.prob
limit 20
'''
rec_result = executeQuery(query)
print(step)
displayItemInRows(rec_result)출처 : The RED : 현실 데이터를 활용한 추천시스템 구현 A to Z by 번개장터 CTO 이동주
'Learning > Recommendation System' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 04-4. Matrix Factorization 기반 평점 예측 (0) | 2022.06.22 |
|---|---|
| 04-3. Linear Regression 모델 기반 평점 예측 (0) | 2022.06.22 |
| 04-1. 고급 추천(Beyond Accuracy) (0) | 2022.06.13 |
| 03-4. Personalized Recommendation (0) | 2022.06.02 |
| 03-3. Related Recommendation (0) | 2022.06.02 |